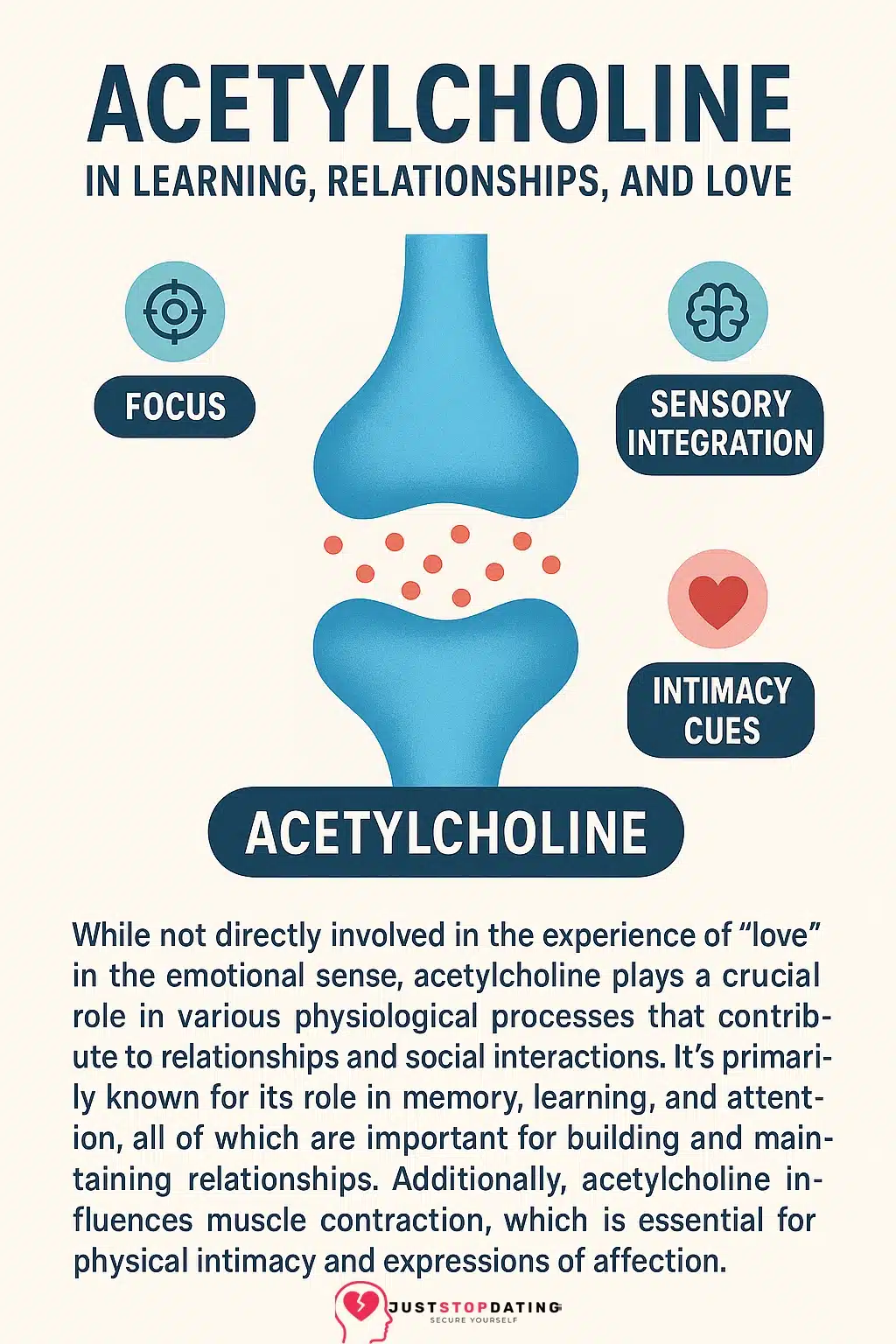
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter involved in attention, learning, memory, and sensory responsiveness. In the context of relationships and dating, acetylcholine plays a critical role in sustained focus, emotional encoding, and the regulation of parasympathetic nervous system functions—such as calmness and intimacy. It influences how individuals attend to and process emotionally salient cues during early relational bonding.
Acetylcholine
| |
|---|---|
| Common Phrase | Acetylcholine |
| Core Characteristics | Attention regulation, memory encoding, parasympathetic activation, sensory tuning |
| Associated Traits | Focus during bonding, calm alertness, emotional sensitivity, sensory awareness |
| Behavioral Indicators | Sustained eye contact, responsive listening, somatic calmness in safe relationships |
| Contrasts With | Dopamine-driven novelty seeking, cortisol-driven threat response, adrenaline arousal |
| Associated Disciplines | Neuroscience, psychopharmacology, cognitive psychology, behavioral science |
| Cultural Relevance | Increasingly referenced in neurodiversity, attention, and intimacy-related research |
Definition
Acetylcholine is a key neurotransmitter that facilitates cognitive focus, learning, and restful states through the parasympathetic nervous system. In emotional and relational contexts, it underpins states of calm attentiveness—supporting safety cues, eye contact, emotional attunement, and memory consolidation during intimacy. It balances arousal and regulation, making it vital to emotional presence in early-stage attraction and bonding.
Other Names
ACh, cholinergic transmitter, parasympathetic neurotransmitter, focus molecule, neuromodulator of attention
History
1900s–1910s: Early Clues in Autonomic Physiology
Initial studies on vagus nerve stimulation and muscular responses in frogs suggested that nerves release chemicals. In 1906, John Newport Langley introduced the concept of “receptive substances,” a precursor to receptor theory. In 1914, British physiologist Henry Dale identified a compound, later named acetylcholine, as a potential chemical messenger that mimicked parasympathetic effects in smooth muscle.
1920s–1930s: Nobel-Prize Confirmation of Chemical Signaling
In 1921, German-Austrian scientist Otto Loewi conducted a landmark frog heart experiment showing that nerve stimulation released a substance (later confirmed as ACh) that slowed heart rate. This became definitive evidence of chemical neurotransmission. In 1936, Dale and Loewi were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery of the first neurotransmitter.
1940s–1950s: Synthesis, Breakdown, and Enzyme Discovery
Researchers identified key enzymes involved in acetylcholine metabolism: choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), which synthesizes it, and acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which rapidly breaks it down. This period established the cholinergic system as central to both peripheral and central nervous functions. Work by Marthe Vogt and Wilhelm Feldberg further clarified ACh’s role in the central nervous system.
1960s–1970s: Cholinergic Mapping and Brain Function
Neuroanatomists began mapping cholinergic pathways in the brain, especially from the basal forebrain to the cortex and hippocampus. Brazilian neuroscientist Cecilia Arraes and American researchers like Wurtman and Fonnum expanded understanding of ACh in attention, REM sleep, and sensory processing. The concept of “volume transmission” emerged, recognizing that ACh can diffuse and affect wide neural areas beyond direct synapses.
1980s–1990s: Clinical Integration and Alzheimer’s Breakthrough
Postmortem studies of Alzheimer’s disease revealed a marked reduction in acetylcholine and degeneration of cholinergic neurons. The cholinergic hypothesis of memory loss gained traction, leading to therapeutic development of cholinesterase inhibitors like donepezil and rivastigmine. Japan, Sweden, and the U.S. led clinical trials validating ACh’s role in cognitive decline and initiating pharmaceutical intervention models still used today.
2000s–2010s: Expanded Functions in Emotion, Focus, and Social Processing
With advanced imaging and molecular tools, scientists began to link ACh with micro-attention, motivational salience, emotional tone, and social cue interpretation. Work by researchers like Michael Hasselmo and Angela Yu modeled cholinergic modulation of uncertainty and learning. In trauma research, acetylcholine is now studied for its role in vagal tone and the regulation of hypervigilance and social withdrawal.
2020s–Present: Neurodivergence, Co-Regulation, and Interpersonal Focus
Contemporary studies explore how acetylcholine affects relational presence, especially in neurodivergent populations (e.g., ADHD, autism). Scientists are also investigating cholinergic tone in romantic engagement, attention repair, and sensory resilience. Global research collaboratives now examine links between ACh pathways, inflammation, and stress-linked cognitive dysfunction across lifespan and culture.
Cultural Impact
Attention Economy and Burnout
ACh is part of a neurobiological counterbalance to overstimulation. Cultural conversations around burnout, overstimulation, and ADHD have increased focus on this transmitter.
Neurodivergent Intimacy
Therapists and educators working with autistic and ADHD populations highlight ACh’s role in sensory sensitivity and social regulation during romantic interactions.
Biology
Cholinergic Pathways
Produced in the basal forebrain and brainstem, ACh modulates activity in the hippocampus, cortex, and thalamus affecting learning, sleep, attention, and emotional memory formation.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
As the chief neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic system, acetylcholine slows heart rate, lowers blood pressure, and promotes social safety cues essential for connection.
Neuroplasticity and Learning
It enhances synaptic plasticity, helping individuals learn from emotionally significant moments—whether a first date, a betrayal, or an expression of affection.
Psychology
Sensory Processing and Safety
This neuromodulator plays a foundational role in filtering sensory input and maintaining emotional stability in social environments. Cholinergic signaling helps fine-tune how we process noise, facial cues, proximity, and rhythm—supporting a felt sense of safety during physical closeness. In relational contexts, it reduces background noise in the nervous system, allowing for smoother co-regulation and improved tolerance for intimacy. When this pathway is underactive, individuals may experience emotional defensiveness, hypersensitivity, or social withdrawal, even in otherwise safe situations.
Micro-Attention and Presence
Sometimes referred to as the “attention molecule,” this compound enables the brain to shift focus toward subtle, relationally significant cues—tone changes, blinking rate, pupil dilation, or micro-expressions. This contrasts with dopamine-driven novelty seeking; the cholinergic system supports deep noticing. These signals are essential in early attachment, trust-building, and social mirroring. In emotionally complex conversations, this messenger helps sustain attunement and curiosity without overwhelming the system.
Cognitive Flexibility and Repair
Beyond perception, this parasympathetic neurotransmitter also supports task switching, emotional perspective-taking, and repair after rupture. It enhances learning from feedback and softens defensive reactivity by allowing new information to enter awareness without triggering threat responses. These properties are particularly important in psychotherapy, relational maintenance, and environments requiring mutual regulation or adaptive conflict resolution.
Dysregulation and Mental Fatigue
Impairments in this system have been associated with brain fog, irritability, and difficulty maintaining presence in emotionally taxing situations. In individuals with high stress or burnout, low cholinergic tone can result in over-reliance on habit, reduced capacity for nuanced empathy, or emotional flattening. Psychological restoration practices—like deep breathing, nature exposure, or interpersonal eye contact—are known to activate these pathways and restore relational energy.
Sociology
Intimacy and Regulation Norms
Social rituals that promote eye contact, touch, and vulnerability depend on neuromodulators like ACh. Cultural scripts about “calm presence” are partly neurochemical expectations.
Depictions in Media
Television Series
- “The Midnight Gospel” (Netflix, 2020) – A psychedelic reflection on emotional presence and awareness, implicitly tied to cholinergic modulation during sensory overload.
Films
- “Her” (2013) – Theodore’s deep, attentive connection with an AI reflects heightened sensitivity and presence, echoing ACh’s emotional attentiveness.
Literature
- “The Body Keeps the Score” by Bessel van der Kolk (2014) – Discusses how safety and emotional regulation (partially mediated by ACh) are foundational to trauma recovery and healthy relationships.
Visual Art
Visual motifs that emphasize softness, stillness, and attentiveness, such as quiet portraiture or intimate moments, mirror acetylcholine’s role in sensory intimacy and focused connection.
- “Mother and Child” by Mary Cassatt (1890): A visual representation of cholinergic calm: mutual gaze, close contact, and regulated presence.
Publications
Research on ACh spans neurobiology, psychiatry, and behavioral science. Key topics include attention regulation, intimacy, trauma processing, emotional safety, and neurodivergence.
Research Landscape
ACh is widely studied in neuroscience, particularly in relation to attention, memory, and parasympathetic regulation. Emerging areas of research explore its role in emotional regulation during romantic bonding, attachment formation, trauma recovery, and social cognition in neurodiverse populations.
- Bidirectional regulation factor of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells differentiation: a focus on bone-fat balance in osteoporosis
- Concurrent Viral Transmission and Wildfire Smoke Events Following COVID-19 Pandemic School Closures in New York City: Associations of a Large Natural Experiment With Acute Care for Pediatric Asthma, 2018-2023
- Evaluating the current research landscape in gender-affirming surgery
- What matters most to midwifery clients? Exploring continuity of care preferences through a cross-sectional survey in Ontario, Canada
- Conservative treatment of ameloblastic fibroma a case report with review of literature
FAQs
Is acetylcholine linked to romantic attraction?
Indirectly. While it doesn’t create desire, it supports emotional focus, attunement, and calmness—factors that increase bonding and perceived connection.
How does acetylcholine affect dating experiences?
It helps individuals stay emotionally regulated and attentive in social settings, enhancing perception of subtle relational cues and supporting co-regulation.
Is acetylcholine relevant to ADHD or neurodivergent dating?
Yes. Dysregulation of acetylcholine can affect attention and sensory modulation. Some ADHD and autistic individuals benefit from strategies that support cholinergic tone during intimacy.
Can I increase acetylcholine naturally?
Choline-rich foods (like eggs), mindfulness practices, sleep, and reducing overstimulation may support healthy acetylcholine levels. Always consult a medical provider for clinical concerns.